A light socket that’s failing can be frustrating and dangerous. Understanding why light sockets fail will help you fix the problem and prevent it from happening again.
Light sockets fail because of bad wiring, worn out parts, corrosion, and improper installation. You can prevent light socket failure by doing some maintenance and taking care of these things.
Now, let’s talk about the common reasons light sockets fail and how you can prevent them.

One of the most common causes of light socket failure is faulty wiring.
Poorly connected or damaged wires can disrupt the flow of electricity, leading to intermittent lighting or complete failure. Over time, wires may loosen or degrade due to wear and tear, causing the socket to malfunction. In some cases, improper installation during the initial setup can lead to wiring problems. Using the wrong wire gauge or making weak connections can result in the socket receiving inconsistent power, which can eventually cause it to fail.
Another frequent cause of socket failure is the wear and tear of internal components.
The metal contacts inside the socket can become worn down or damaged over time, especially in sockets that are frequently used. This can lead to poor contact between the light bulb and the socket, resulting in flickering or a failure to power the bulb. Additionally, the socket itself may become damaged. Cracked or broken sockets can cause electrical arcing, which is dangerous and can lead to socket failure.
Corrosion and rust are also major contributors to light socket failure, particularly in outdoor or damp environments. Moisture can cause metal parts of the socket to corrode over time, which interferes with the electrical connection between the bulb and the socket. If the socket’s contacts become rusted, they may no longer provide a solid connection, leading to flickering lights or complete failure. Regularly inspecting sockets in humid or exposed environments can help catch this issue early.

Light sockets can also fail due to overheating, which often occurs when bulbs with a higher wattage than the socket is rated for are used. Overheating can cause the insulation on wires to degrade and damage the internal components of the socket, leading to failure. When sockets are exposed to excessive heat for prolonged periods, the plastic or metal components can warp or melt, further damaging the socket’s ability to function correctly.
Loose or insecure connections between the wires and the socket terminals can prevent electricity from flowing properly. This can result in intermittent lighting or complete socket failure. Over time, vibrations or movement in the fixture can cause connections to loosen, disrupting the socket’s ability to power the bulb. Regularly checking and tightening connections during maintenance can help prevent this issue from causing socket failure.

Using incorrect bulbs in the socket can also lead to failure. For instance, using a bulb with a higher wattage than the socket is designed to handle can cause overheating. Similarly, installing an LED bulb in a lamp socket designed for incandescent bulbs without checking compatibility can result in malfunction or failure over time. It is essential to match the bulb type and wattage with the socket specifications to ensure proper function and avoid damage.
A short circuit can occur when wires inside the socket touch each other or when a wire touches the metal part of the socket.
This can cause the socket to stop functioning altogether, and in severe cases, it could even lead to electrical fires. Short circuits can result from improper wiring, insulation breakdown, or physical damage to the wires. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial to preventing further damage to the socket and overall electrical system.
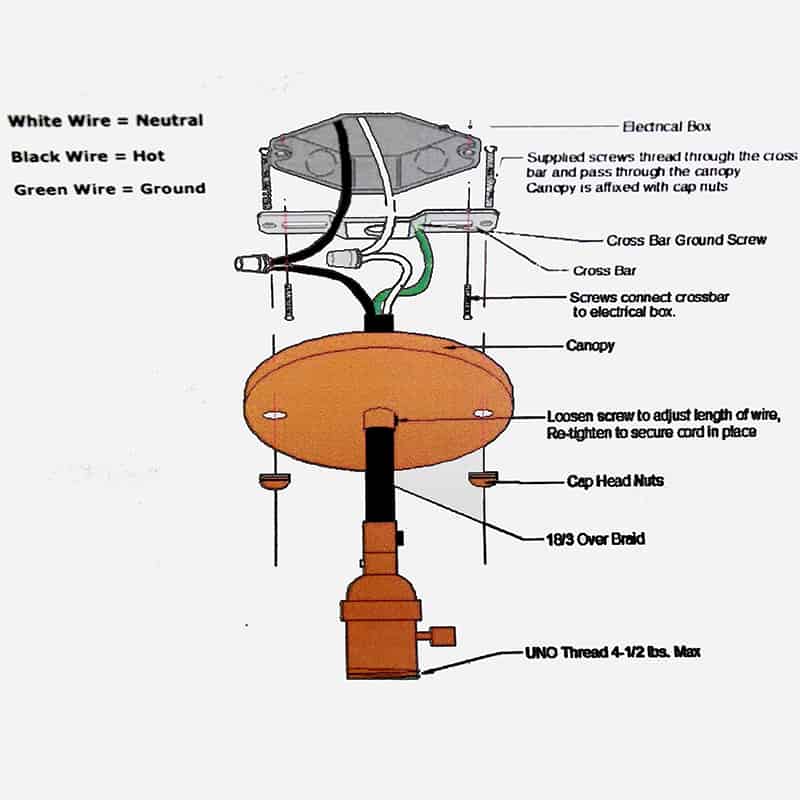
Another dangerous issue is electrical arcing, which occurs when there is a gap between electrical contacts, causing electricity to jump between them.
This can happen in a worn-out or damaged socket where the bulb isn’t properly seated. Arcing can damage the socket over time, causing it to fail. This issue not only leads to light socket failure but also poses a significant fire risk, as arcing often generates excessive heat, which can damage nearby components and increase the risk of an electrical fire.
Environmental factors also play a role in socket failure, especially for those installed outdoors or in damp environments. Water, dirt, and other contaminants can get inside the socket, leading to corrosion or short circuits. Similarly, extreme temperatures can cause sockets to crack or degrade faster than those in controlled environments. Using weather-resistant or properly rated sockets for outdoor use can help prevent socket failure due to environmental exposure.
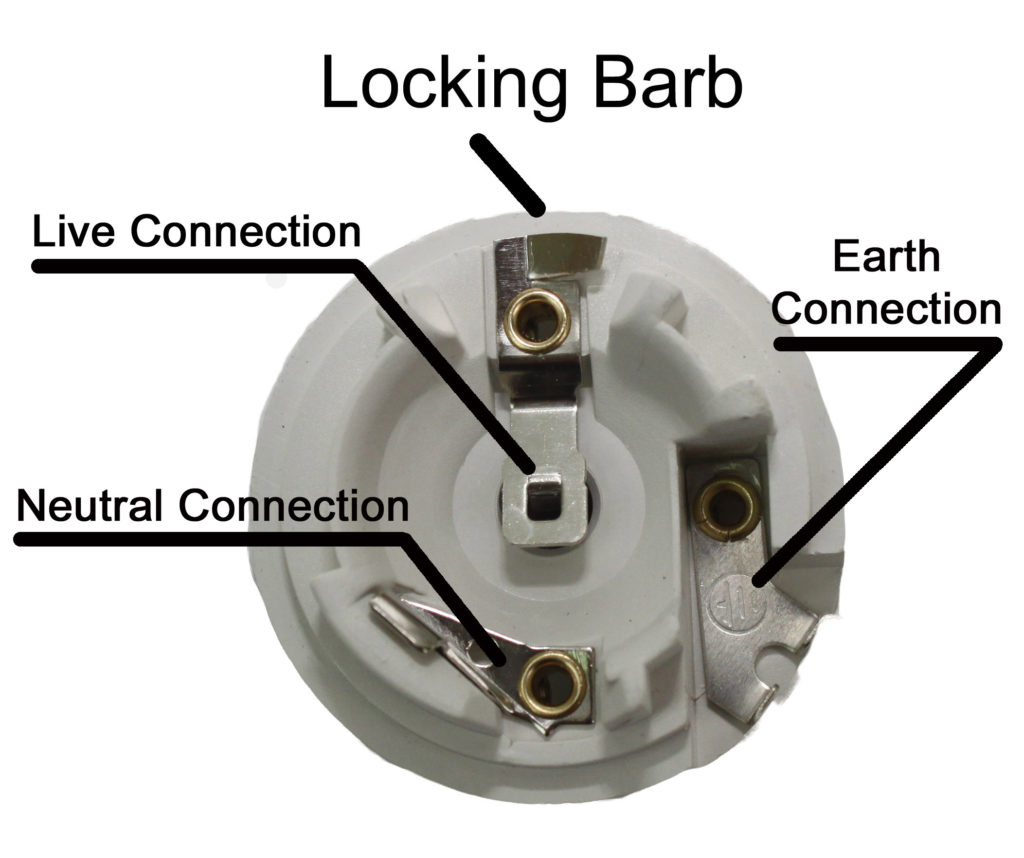
Finally, lack of regular maintenance is another reason why light sockets fail overall. Light sockets, like all electrical components, require regular maintenance to ensure they function correctly. Dust, debris, or small insects can get inside the socket, causing problems with the electrical connection. Over time, these issues can compound, leading to socket failure. Regular inspection and cleaning of sockets, especially in high-use areas, can prevent many of the issues that cause sockets to fail prematurely.
Knowing why light sockets fail will help you prevent it from happening. You can prevent light sockets from failing by doing some simple maintenance and making sure they’re installed right.













