Selecting the right bulb for your light fixture is not just about the wattage or type of bulb. One of the most important things to consider is the base of the bulb. The base is what makes the electrical contact and holds the bulb in place. Whether you’re changing a light bulb in your house or upgrading to some of the new energy-efficient options, you need to understand bulb bases.
The base of a light bulb is the part that connects the light bulb to the light fixture, makes the electrical contact, and holds the bulb in place. There are typical bases you’ll find in homes, like E26, E27, and GU10.
We’re going to talk about the different kinds of light bulb bases, what they do, and how they impact your ability to use them in your lights.
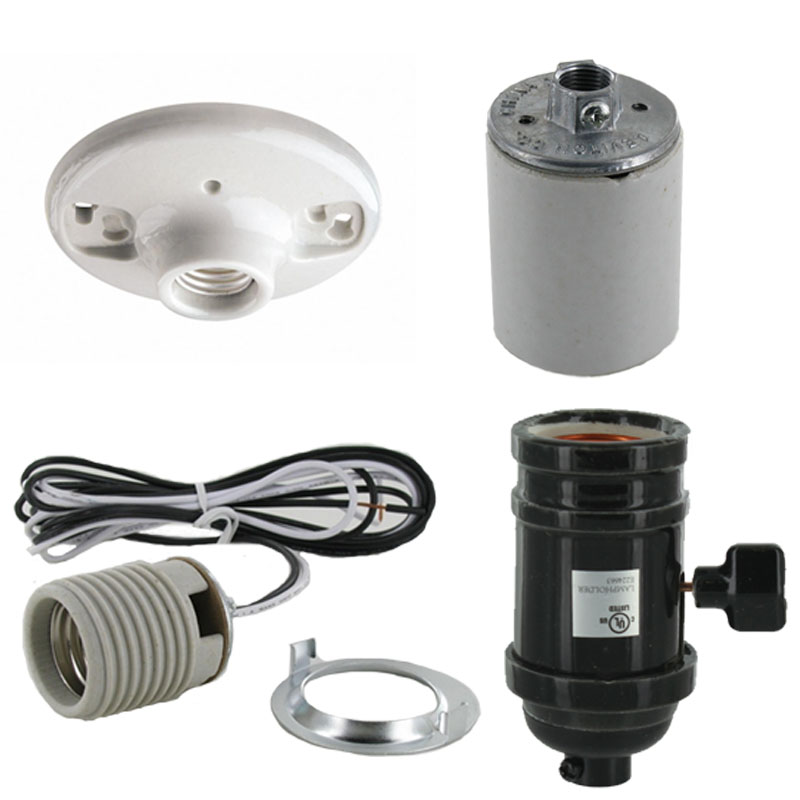

What is a bulb base?
A bulb base is the essential connection point between a light bulb and a fixture. It provides the physical attachment and electrical connection needed to power the bulb. The base consists of conductors that allow electricity to flow from the socket into the bulb, which then converts the electricity into light. The base also holds the bulb securely in place, ensuring it doesn’t loosen or wobble during operation.
Bulb bases come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, depending on the fixture type, bulb design, and regional standards. For example, screw-type bases are commonly used in table lamps and ceiling lights, while pin-type bases are often found in recessed lighting and spotlights. Choosing the right bulb base ensures not only a good fit but also the safe and efficient operation of the light bulb.
What are the most common types of bulb bases?
Several bulb base types are commonly used in homes, businesses, and industrial settings. The most frequently encountered bases include:
- E26 and E27 (Medium Screw Base): These bases are widely used for general-purpose lighting in homes and commercial spaces. E26 is standard in North America, while E27 is used in Europe and most other regions. The primary difference is their voltage compatibility; E26 bulbs are designed for 120V systems, while E27 bulbs are compatible with 220-240V systems. Both have a 26-27mm diameter and are interchangeable in terms of physical size.
- GU10: This is a popular base for LED spotlights and downlights. It features a twist-and-lock design with two short pins, providing a secure fit in recessed lighting fixtures. The GU10 base is commonly found in kitchens, bathrooms, and accent lighting applications, particularly in modern homes using energy-efficient LED technology.
- B22 (Bayonet Cap): Used primarily in the UK, Australia, and parts of Asia, the B22 base is characterized by two side pins that twist into the socket. This base is often found in ceiling fixtures and lamps in those regions and provides a sturdy and reliable connection.
- G4 and G9: These are low-voltage, pin-type bases used primarily in halogen and LED bulbs for decorative and accent lighting. The G4 base has two thin pins and is typically used in small fixtures like under-cabinet lighting. The G9 base, while also pin-based, is slightly larger and used for applications requiring higher voltage, such as some pendant lights.
- E12 and E14 (Candelabra Base): These smaller screw bases are commonly used for decorative lighting, such as chandeliers or wall sconces. The E12 base is standard in North America, while E14 is used in Europe. Both are designed for smaller bulbs that complement ornamental fixtures.
Each of these base types serves a specific purpose, and understanding their differences helps ensure that you choose the right bulb for your fixture.

What is the difference between screw and pin bases?
Screw bases and pin bases represent the two major categories of bulb bases, and their design determines how the bulb connects to the fixture.
- Screw Bases: The most common type, especially in residential settings, screw bases like E26, E27, E12, and E14 are threaded and screw directly into the socket. This design makes installation straightforward, with the bulb held securely in place by the threads. Screw bases are ideal for general-purpose lighting, such as table lamps, ceiling fixtures, and outdoor lights.
- Pin Bases: Pin bases, such as GU10, G4, and G9, use a push-and-twist or push-and-lock mechanism to secure the bulb in place. The pins, typically two or more, slide into corresponding holes in the socket. Pin bases are commonly found in more specialized lighting applications, such as spotlights, recessed lighting, and certain types of LED fixtures. The pin design ensures a tight and stable connection, particularly important in situations where the fixture may be subject to movement or vibration.
The choice between screw and pin bases is largely determined by the type of fixture you are working with. Screw bases are more versatile and commonly used in standard lighting applications, while pin bases are preferred for specific lighting tasks that require secure locking mechanisms.
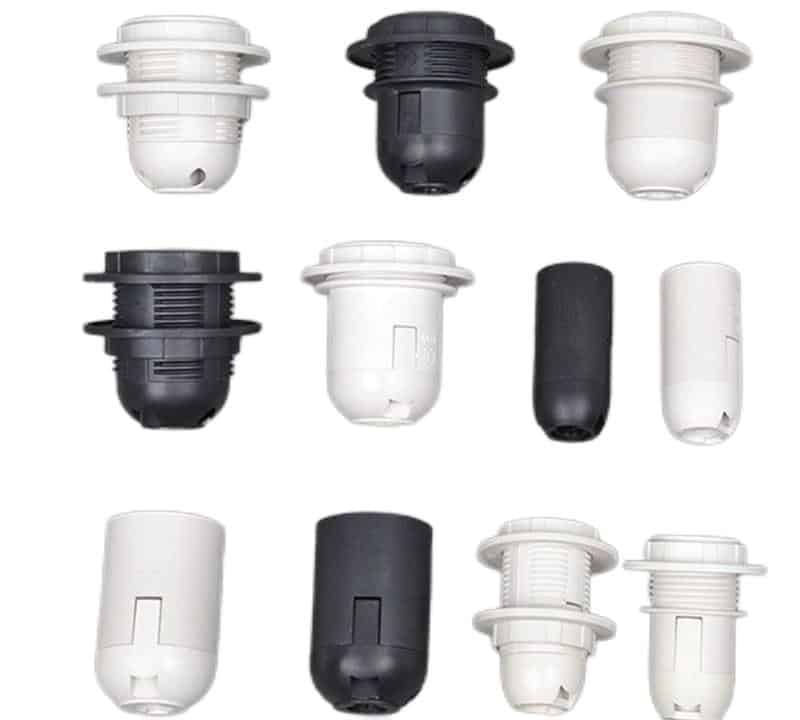

What are the international standards for bulb bases?
International standards for bulb bases vary by region, primarily due to differences in electrical systems. The two most common standards are E26 and E27 screw bases, which differ mainly in their voltage compatibility:
- E26: Used in North America and Japan, E26 bases are designed for 120V electrical systems. This base is found in most household lamps, ceiling lights, and other standard fixtures. It is often referred to as a “medium base” and is the standard for most incandescent, halogen, and LED bulbs in these regions.
- E27: Found in Europe, Asia, and other parts of the world, the E27 base is compatible with 220-240V systems. Like the E26 base, E27 is widely used in homes and businesses for general lighting. Though nearly identical in size to the E26 base, E27 bulbs are designed to handle higher voltage systems and are not interchangeable in regions with different voltages.
Other common international bases include B22, used primarily in the UK and Australia, and G-type pin bases, which are popular in specific lighting fixtures like spotlights and decorative lights. When purchasing bulbs internationally, it’s essential to ensure that the bulb’s base matches both the socket and the region’s electrical standards to prevent any compatibility issues.

How to identify the correct bulb base for your fixture?
Identifying the correct bulb base for your fixture is crucial for ensuring proper installation and functionality. There are a few simple steps you can take to determine the correct base:
- Check the existing bulb: If you’re replacing an existing bulb, check the base type printed on the bulb or the packaging. Common labels like “E26,” “E27,” or “GU10” indicate the type of base.
- Measure the base: If the label is missing, you can measure the diameter of the base. For screw-type bases, such as E26 or E27, the diameter will be approximately 26-27 millimeters. For pin bases, measure the distance between the pins to identify the correct type.
- Look at the fixture: Many fixtures will have a label indicating the compatible bulb types and base sizes. This information is usually found near the socket or on the fixture’s packaging.
- Consider voltage and wattage: Ensure the bulb’s voltage and wattage match the fixture’s specifications. Using a bulb with a higher wattage than recommended can lead to overheating or damage, while incorrect voltage can result in poor performance or even electrical hazards.
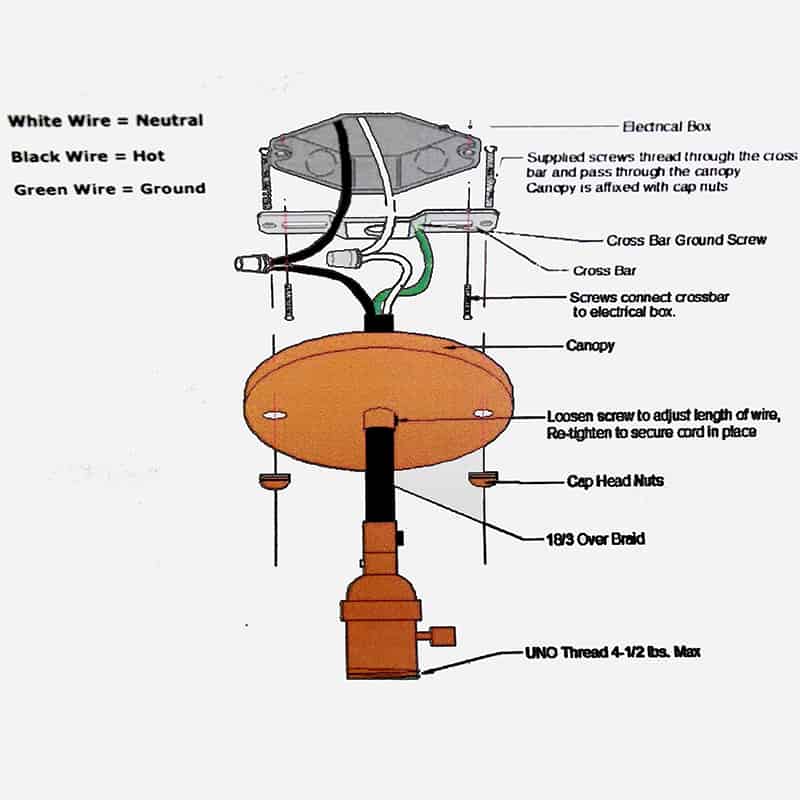
What materials are used in bulb bases?
The material of a bulb base affects its durability, heat resistance, and overall performance. Common materials include:
- Metal: Metal, such as brass or aluminum, is often used in the screw threads or pins of bulb bases due to its excellent electrical conductivity and durability. Metal bases are commonly found in both screw-type and pin-type bulbs.
- Ceramic: Ceramic bases are heat-resistant and are commonly used in bulbs designed for high-temperature environments, such as halogen or high-wattage incandescent bulbs. Ceramic bases provide added protection against heat damage and are durable over long periods.
- Plastic: Plastic is commonly used in modern LED and CFL bulbs, particularly in the base of low-wattage bulbs. While plastic is lightweight and inexpensive, it is less heat-resistant than metal or ceramic, making it better suited for cooler light sources like LEDs.
The choice of material is important depending on the type of lighting and fixture, as it impacts both the safety and longevity of the bulb.
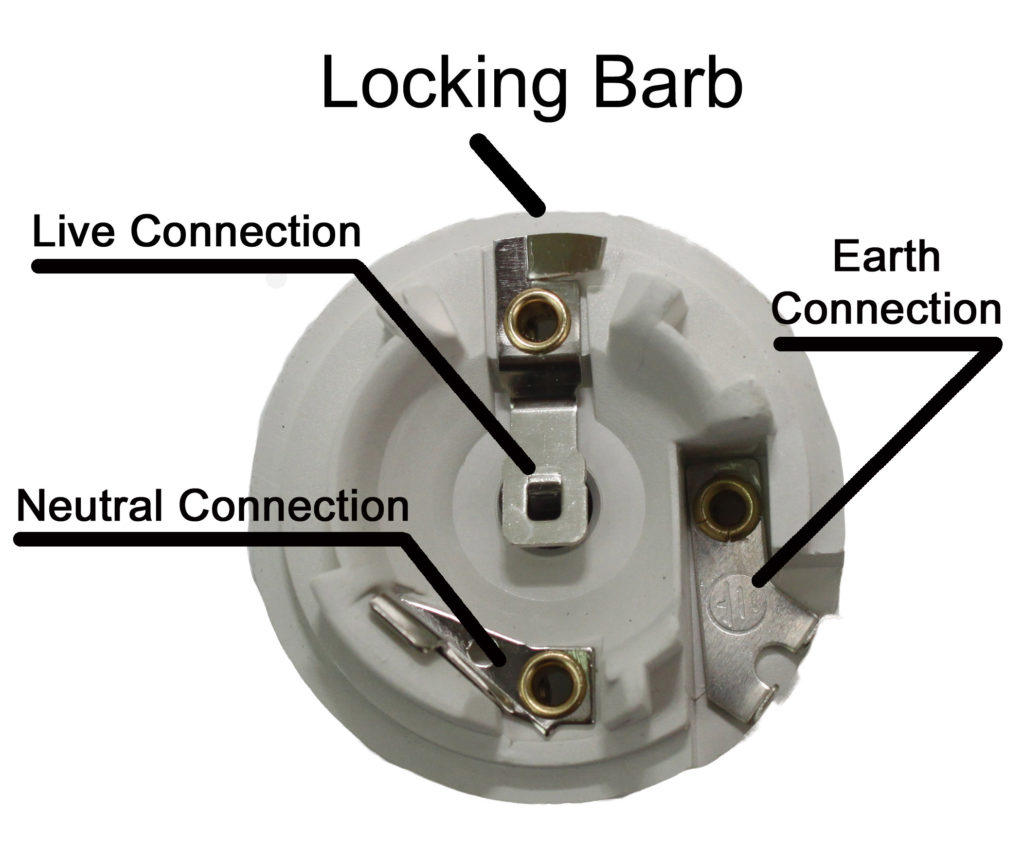
Are there any specialized or rare bulb bases?
While common bulb bases like E26, E27, and GU10 dominate the market, several specialized and less common bases are used for specific applications:
- B22 (Bayonet Cap): Common in the UK and Australia, this twist-lock base is designed for high-powered fixtures and is often used in ceiling lights or industrial settings.
- E39 and E40: These larger screw bases are used for industrial or outdoor lighting applications, such as streetlights or stadium lights. They are built to handle higher wattage and larger bulb sizes.
- G24: Found in compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs), the G24 base is a pin-type connector commonly used in office or commercial lighting applications. It is often found in low-wattage, energy-efficient bulbs.
These specialized bases are used in specific situations and are often found in fixtures designed for high-output or energy-efficient lighting.
How does a bulb base affect compatibility with bulbs?
The bulb base plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility between the bulb and the fixture. A bulb with an incorrect base won’t fit securely in the socket, and even if it does fit, it may not function properly. For example, a bulb with an E27 base cannot be safely used in an E26 socket in regions with different voltage standards, as it could cause electrical problems or overheating.
Using the correct bulb base ensures a safe and secure fit, proper electrical contact, and optimal performance. Always match the bulb’s base type to the fixture’s specifications, ensuring that the wattage and voltage are appropriate for both the bulb and the socket.

Picking the right light bulb socket is important for safe and effective lighting. When you understand the different kinds of bases, the materials they’re made from, and the compatibility issues, you’ll be able to make sure your light bulbs and light fixtures work together the way they’re supposed to.













