Knowing the differences between a plug, an outlet, and a socket is important if you want to use electrical stuff safely and effectively. Misunderstanding these terms could lead to improper installations, unsafe conditions, or equipment not working. Each one has a specific purpose. Plugs connect things to power sources. Outlets provide access to electricity. Light sockets hold light bulbs or plugs in place.
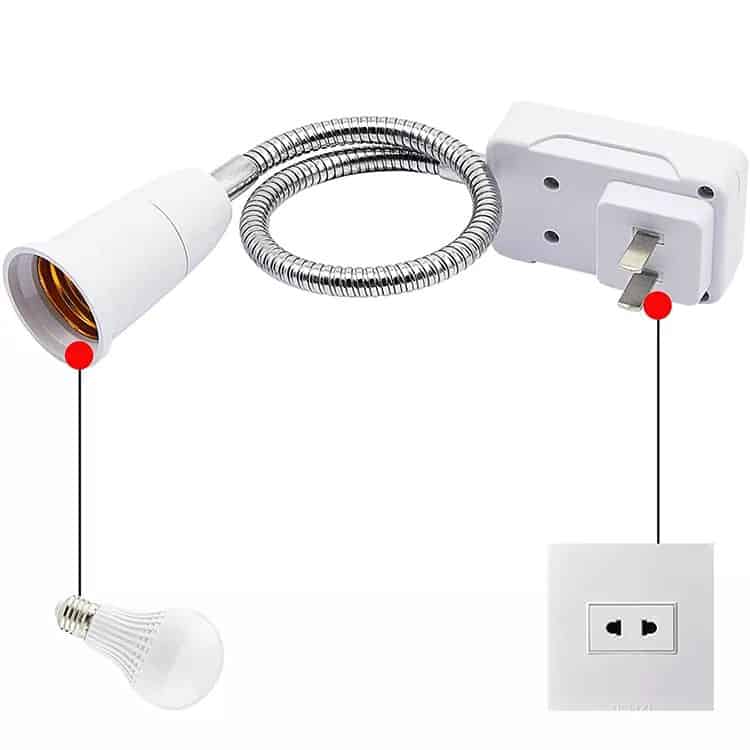
A plug is a movable device designed to connect an appliance or electrical device to a power source. It typically has two or three prongs that fit into the slots of an outlet. Plugs come in various designs to suit different devices and regional standards. Common types include two-prong plugs for basic appliances and three-prong plugs with grounding for safety. Regional variations, such as Type A and B in North America or Type C and F in Europe, reflect differing voltage and frequency standards. Plugs are essential for creating a safe and reliable electrical connection.
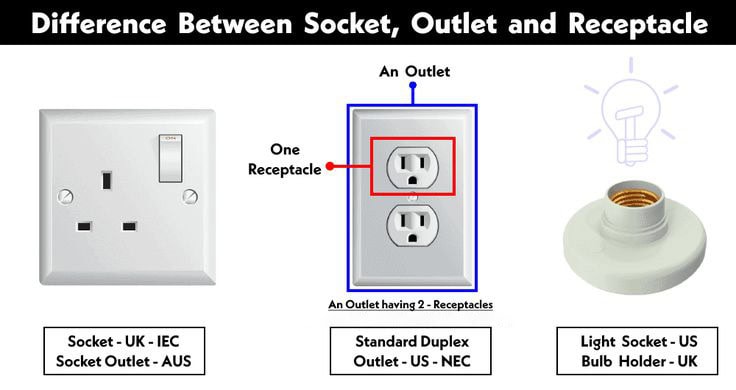
An outlet, on the other hand, is a fixed device installed in walls or other structures to provide access to electricity. It features slots where plugs are inserted to draw power from the electrical circuit. Outlets are categorized into several types based on their function and environment. Residential outlets, such as standard and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) types, are common in homes and protect against electrical shock. Industrial outlets are designed for higher voltage and heavy-duty equipment, while modern USB-integrated outlets cater to charging needs for mobile devices. Outlets often include safety features like tamper-resistant designs and overload protection.
A socket serves a different purpose compared to plugs and outlets. It is a receptacle that holds devices like light bulbs or electrical plugs securely. In lighting, sockets like E26, E27, and GU10 are used to hold bulbs, providing both mechanical support and electrical connection. Power sockets, on the other hand, are designed to accommodate plugs, enabling devices to access power. Sockets are found in various applications, from home lighting to industrial equipment, and are often tailored to specific requirements such as heat resistance or high-voltage capacity.

The key differences between plugs, outlets, and sockets lie in their roles, designs, and applications. A plug is mobile and has prongs designed to fit into an outlet. An outlet is fixed, providing access to electricity through its slots. A socket, meanwhile, can hold either bulbs or plugs securely, enabling them to function correctly. These components work together in an electrical system, creating a seamless flow of power from the source to the device.
Regional standards add another layer of complexity to these components. Plugs and outlets must be compatible with each other, and their designs vary across regions. For instance, North America uses Type A and B plugs and outlets, while Europe relies on Type C and F. Similarly, socket types for lighting differ by region, with E26 being common in the United States and E27 in Europe. Understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring compatibility and safety when traveling or using imported devices.
Despite their clear roles, plugs, outlets, and sockets are often misused or mismatched. Forcing an incompatible plug into an outlet or using the wrong bulb type in a socket can damage the components or pose a safety risk. Grounding is a critical feature of many plugs and outlets, and ignoring it can result in electrical shock. It’s essential to avoid overloading outlets or sockets and to ensure all components meet safety standards.

Modern innovations have enhanced the functionality of these electrical components. Smart plugs allow users to control devices remotely, while USB outlets provide integrated charging solutions for modern gadgets. Wi-Fi-enabled sockets offer advanced control and monitoring, making homes smarter and more energy-efficient. These developments not only improve convenience but also contribute to safer and more sustainable electrical systems.
In conclusion, plugs, outlets, and sockets are integral components of any electrical system, each with a specific purpose. Plugs connect devices to power sources, outlets provide access to electricity, and lamp sockets hold bulbs or plugs securely. Understanding their differences and using them correctly ensures safety, compatibility, and efficiency in all electrical applications. As technology evolves, these components continue to adapt, offering innovative features for modern needs.













